Blood Clot
**Blood Clot**
Blood clots (also known as thrombi) occur when blood thickens and forms a semi-solid or solid mass inside a blood vessel. This can obstruct blood flow, potentially leading to serious health complications.
**Causes:**
* Injury or trauma
* Certain medical conditions (e.g., cancer, heart disease)
* Prolonged immobility or surgery
* Blood clotting disorders
**Types:**
* Arterial clots (in arteries)
* Venous clots (in veins)
* Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
* Pulmonary embolism (PE)
**Symptoms:**
* Pain, swelling, discoloration in the affected area (e.g., leg, arm)
* Shortness of breath, chest pain (if a clot travels to the lungs)
**Diagnosis:**
* Physical exam
* Imaging tests (e.g., ultrasound, CT scan)
* Blood tests
**Treatment:**
* Anticoagulants (blood thinners) to prevent clot formation or growth
* Thrombolytics to dissolve existing clots
* Surgical intervention (in severe cases)
**Prevention:**
* Exercise regularly
* Maintain a healthy weight
* Avoid smoking
* Treat underlying medical conditions
* Use compression stockings during prolonged travel
**Complications:**
* Stroke
* Heart attack
* Organ damage (if a clot blocks blood flow to a specific organ)
**Prognosis:**
With prompt diagnosis and treatment, most blood clots can be managed effectively. However, certain types (e.g., PE) can be life-threatening.
Thrombectomy and Thrombolysis: Understanding Stroke Treatment Options
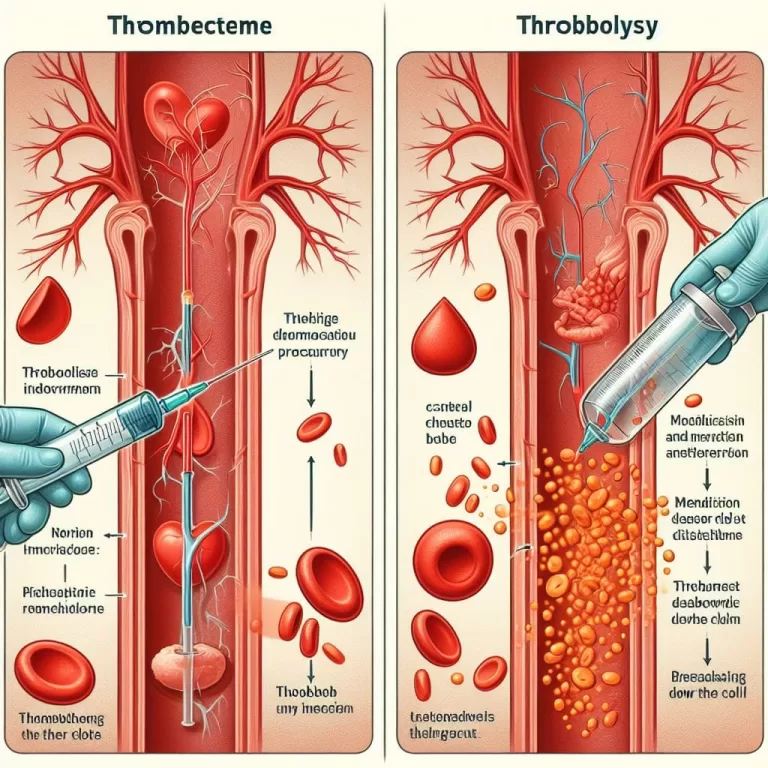
Thrombectomy and thrombolysis are two medical procedures doctors use to treat blood clots. The one you need will depend on your circumstances. Aleksandr Zyablitskiy/Getty Images The primary difference between the two treatments is that thrombectomy involves surgically removing a blood…
