
...or normocytic, depending on the size and volume of the red blood cells (erythrocytes):[6][7] Macrocytic anemia. In this category of anemia, the red blood cells are larger than normal. This...

...blood moves through the arteries, which are composed of strong walls. The pressure in which they flow within these paths is referred to as blood pressure. Blood pressure can be...

...packaged foods. It’s high in fiber and may help with digestive health and decrease blood sugar and blood fat levels. It’s generally considered safe but may cause reactions in infants...

...blood clot that becomes lodged in the artery. Blood clots typically develop when tiny particles in the blood, known as platelets, stick to fatty deposits called plaques.[^1] The cause of...

...and is spread from person to person, primarily through sneezing and coughing.[2] When an infected person sneezes, coughs, or talks, they may send infected water droplets into the air. It...

...will check whether the readings are out of range. Blood tests: To check the levels of fats, sugars, cholesterol and protein in the blood. Read more about blood tests. Electrocardiogram...

...done with minimally invasive surgical techniques, such as endovascular clot removal. What is a Blood Clot? A blood clot is a thickened, clotted mass of blood that has broken away...
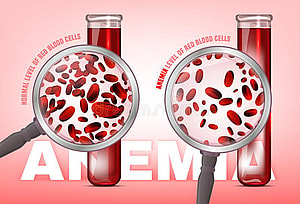
[trp_language language=”en_US”] A person’s hemoglobin levels indicate how much hemoglobin is present in their blood. Hemoglobin, also written as hemoglobin, is a complex protein found in red blood cells which helps...

[trp_language language=”en_US”] A person’s hemoglobin levels indicate how much hemoglobin is present in their blood. Hemoglobin, also written as hemoglobin, is a complex protein found in red blood cells which...
...body mistakes its red blood cells for a harmful substance. It produces antibodies that attack and prematurely destroy the cells, leading to anemia. Red blood cells, responsible for delivering oxygen...










