What is a Radiologist?
A Radiologist specializes primarily in the assessment and analysis of medical imaging to identify and help diagnose diseases within the body. The medical imaging can be carried out by a radiographer or radiologic technologist. The Radiologist will read and interpret the images and report the findings to the physician who ordered the images, such as an Oncologist looking to discover the location of a tumor to determine the best course of treatment.
Radiologists can utilize a variety of different imaging technologies including X-rays, ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), nuclear imaging, positron emission tomography (PET), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to identify and diagnose diseases.
Radiologists can be found working in a private practice environment as well as in hospitals and outpatient centers and often do not have much direct interaction with patients. Other areas of further specialized training and sub-specialties within Radiology include breast imaging, cardiovascular radiology, musculoskeletal imaging, pediatric imaging, radiation safety, and the study of the effects of radiation on the body.
Radiologists are a vital component of medical care providing information and working in conjunction with other medical specialists including Oncologists by detecting cancer within the body, Emergency Medicine/Critical Care doctors, General Surgeons, and Vascular/Phlebologists to name a few.
Definition
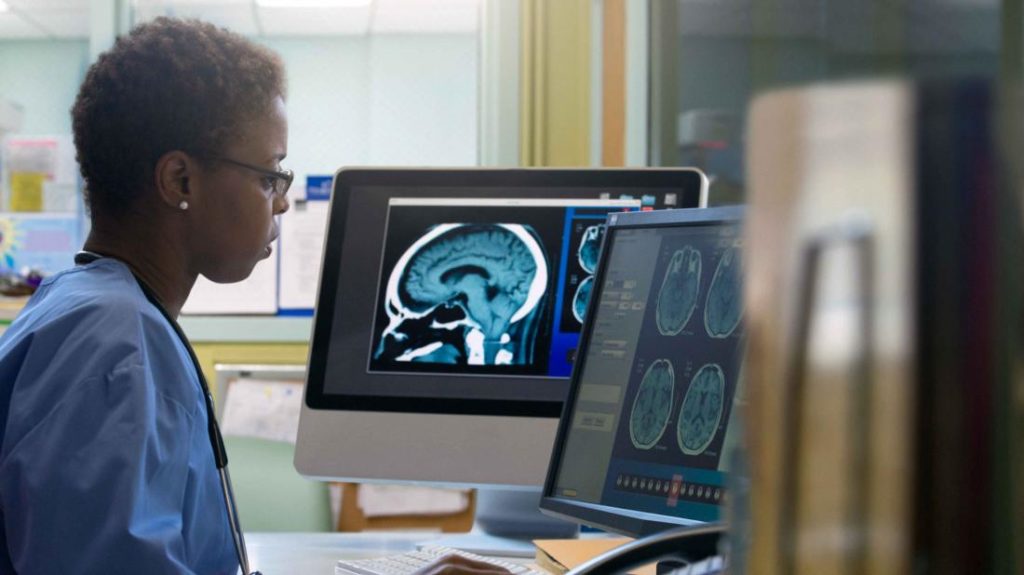
A radiologist is a type of doctor who specializes in medical imaging. Radiologists analyze images, such as X-rays, to help diagnose, monitor, and treat various conditions or injuries.
Radiologists are different than radiographers. Although both of these professionals work with medical imaging, radiographers are the people who operate the machinery.
There are different types of radiologists, including diagnostic radiologists and medical physicists.
Radiologist Plays a Key Role in Your Healthcare By:
Diagnostic Radiologists
Diagnostic radiologists use a variety of imaging procedures to see inside the body and assess or diagnose the patient’s condition. Your radiologist plays an important role in your health by acting as an expert consultant to your referring physician (the doctor who sent you for testing) by assisting in choosing the proper exam and directing radiology technologists (those who operate the equipment) in properly performing quality exams. They interpret and report on the resulting images, recommending treatment and, only when appropriate, additional tests.
Diagnostic radiologists, through extensive clinical work and related research, may also specialize in these radiology subspecialties:
Interventional Radiologists
These radiologists are doctors who diagnose and treat patients using image-guided, minimally invasive techniques such as X-rays and MRI. They carefully guide instruments through tiny incisions in the body, reaching the source of a medical problem and delivering targeted treatments. These treatments are for conditions such as heart disease, stroke, cancer, and uterine fibroids, offering less risk, pain, and recovery time compared to traditional surgery.
Radiation Oncologists
These highly trained radiologists are doctors who prescribe and oversee each cancer patient’s treatment plan. They use radiation therapy to treat cancer, and they monitor the patient’s progress and adjust treatment to make sure patients receive appropriate quality care. Radiation oncologists receive extensive training in cancer medicine, in the safe use of radiation to treat disease, and in managing any side effects caused by radiation.
Types
There are several different specialties of radiology, including:
Diagnostic radiology
Diagnostic radiologists use medical imaging to diagnose and treat diseases. They can use a variety of different imaging methods, such as:
Interventional radiology
Interventional radiologists use medical imaging to provide therapy to people with noncancerous conditions.
For example, an interventional radiologist might use medical imaging to support a surgical procedure.
This imaging can make surgical procedures safer and lead to faster recovery times. Interventional radiologists typically work on keyhole surgery.
Keyhole surgery involves making small cuts instead of larger ones and using tiny cameras to see inside the body.
Radiation oncology
A radiation oncologist uses radiation-based therapy to treat cancer. This therapy involves the use of high-energy radiation to damage cancer cells, which stops them from spreading further.
It can help reduce symptoms or, in some cases, cure the condition entirely.
Medical physics
Medical physicists use their understanding of physics to support the practice of medicine in different ways.
For example, they can advise on and deliver the technical aspects of medical imaging to ensure the safety of patients and the effectiveness of the results.
Some medical physicists are also researchers and play a role in developing new medical technology. Medical physicists have developed many devices that doctors commonly use today, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
What do they do?
Radiologists can work in clinical practices, hospitals, or universities. The job of radiologists varies depending on their specialty.
All radiologists work with medical imaging methods, which include:
Most of these techniques involve the use of radiation. Radiologists are highly trained in keeping people safe from the harmful effects of radiation.
These professionals can help other doctors decide on the right imaging method to use and understand what the results mean for treatment. They can also help interpret different images and other test results to make a diagnosis or monitor whether current treatments are working.
Certain types of radiologists, including interventional radiologists, are more actively involved in the treatment process. Others, such as diagnostic radiologists, might provide support to other healthcare professionals.
Some radiologists rarely work with patients and instead work in labs doing research. For example, some clinical studies might include a radiologist to help with the analysis of medical images.
Education
Radiologists are medical doctors, so they follow a similar path to those working in other specialties.
All radiologists need a medical degree, which involves 4 years of training and education from a medical school.
Most medical schools require students to have an undergraduate degree and pass a Medical College Admission Test before entering.
After finishing medical school, radiologists do a year of clinical training. They may spend a preliminary year focusing on one area of medicine, such as internal medicine, or it may be a transitional year that involves several rotations through different specialties.
Following the clinical year, radiologists usually complete 4 years of paid residency. Residency is a combination of further medical education and on-the-job training in different areas of radiology.
After a residency, most radiologists do a fellowship. A fellowship is an additional 1 or 2 years of training in a specialized area of radiology, such as nuclear radiology. Interventional radiologists must undertake a 2-year fellowship.
## What is a Radiologist?
**Radiologist:** A medical doctor specializing in diagnosing and treating diseases and injuries using imaging technologies such as X-rays, computed tomography (CT) scans, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and ultrasound.
**Role of a Radiologist:**
Radiologists play a crucial role in healthcare by:
* **Interpreting Medical Images:** Analyzing and interpreting the findings on medical images to identify abnormalities, such as tumors, fractures, or infections.
* **Diagnosing Diseases:** Using their expertise in medical imaging, radiologists diagnose a wide range of conditions, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and respiratory disorders.
* **Guiding Treatment:** Providing recommendations for appropriate medical interventions based on their interpretations of medical images.
* **Perform Image-Guided Procedures:** Performing procedures guided by imaging, such as biopsies, insertions, and ablations, to treat various medical conditions.
**Specializations in Radiology:**
* **Diagnostic Radiology:** Focused on the diagnosis of diseases and injuries through imaging techniques.
* **Interventional Radiology:** Involves minimally invasive image-guided procedures to treat conditions.
* **Nuclear Medicine:** Utilizes radioactive tracers to evaluate organ function and detect disease.
* **Radiation Oncology:** Employs radiation therapy to treat cancer by destroying cancerous cells.
* **Pediatric Radiology:** Specialized in imaging and diagnostics for children.
**Education and Training:**
To become a radiologist, individuals typically complete:
* A four-year Bachelor’s degree in science
* Four years of medical school
* A five-year radiology residency program
* Optional additional subspecialization fellowships
**Requirements for Radiologists:**
* **Strong Analytical Skills:** To interpret medical images accurately and identify abnormalities.
* **Excellent Communication Skills:** To convey their findings to patients, referring physicians, and other healthcare professionals.
* **Up-to-Date Medical Knowledge:** To stay abreast of advancements in imaging techniques and medical diagnoses.
* **Problem-Solving Abilities:** To determine the most appropriate course of action based on their interpretations.
**Importance of Radiologists:**
Radiologists play a vital role in modern healthcare by:
* **Providing Accurate Diagnoses:** Early and accurate diagnoses enable timely and effective treatment.
* **Guiding Treatment Decisions:** Radiologists’ recommendations help healthcare providers determine the most appropriate treatment options.
* **Minimizing Invasive Procedures:** With advanced imaging techniques, radiologists can often diagnose and guide treatment without the need for major surgery.
* **Improving Patient Outcomes:** Accurate diagnoses and timely interventions lead to better patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.







A radiologist is a medical doctor who specializes in diagnosing and treating diseases using imaging techniques such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs.