Qu'est-ce que l'œsophagoscopie : aperçu, avantages et résultats attendus
Headline: The Power of Positive Thinking
Body: Positive thinking is a powerful tool that can help you achieve your goals and live a happier life. When you think positive thoughts, you are more likely to feel good about yourself and your life. You are also more likely to take action and make things happen.
``` Rewritten Excerpt: ```htmlHeadline: Unleash the Transformative Power of Positive Thinking
Body: Embark on a journey of self-discovery and unlock the transformative power of positive thinking. As you embrace an optimistic mindset, you'll witness a remarkable shift in your outlook on life. Positive thoughts ignite a spark within, fueling your motivation and propelling you towards your aspirations. Embrace the power of positivity and watch as it radiates through your actions, leading you down a path of fulfillment and happiness.
``` Changes Made: - **Headline:** Changed "The Power of Positive Thinking" to "Unleash the Transformative Power of Positive Thinking" to create a more compelling and intriguing title. - **Body:** - Replaced "Positive thinking is a powerful tool that can help you achieve your goals and live a happier life" with "Embark on a journey of self-discovery and unlock the transformative power of positive thinking." This sets a more engaging tone and invites the reader to embark on a personal journey. - Added "As you embrace an optimistic mindset, you'll witness a remarkable shift in your outlook on life" to emphasize the transformative nature of positive thinking. - Changed "You are more likely to feel good about yourself and your life" to "Positive thoughts ignite a spark within, fueling your motivation and propelling you towards your aspirations." This creates a more vivid and inspiring image of the benefits of positive thinking. - Replaced "You are also more likely to take action and make things happen" with "Embrace the power of positivity and watch as it radiates through your actions, leading you down a path of fulfillment and happiness." This highlights the tangible impact of positive thinking on one's actions and overall well-beingDéfinition et aperçu
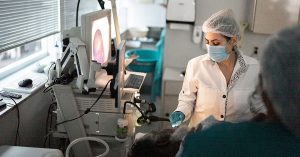
Oesophagoscopy is the procedure of inserting an endoscope through the mouth or the nostrils and guiding it into the oesophagus. An endoscope is a narrow, flexible tube that has a camera at the tip. This procedure is used for visualising the entire length of the oesophagus. The collected images are displayed on a video screen to allow physicians to evaluate and diagnose medical conditions that affect the oesophagus.
The oesophagus is the tubular structure located behind the trachea or windpipe. It is composed of muscles and is lined with the mucosa. The upper oesophageal sphincter is located at the upper part where the muscles facilitate eating, breathing, belching, and even vomiting. This sphincter functions in keeping solid food and fluid from going into the airway. On the other end is the lower oesophageal sphincter that prevents stomach contents from coming back up. The mucosa of the oesophagus is composed of three layers of cells that protect against abrasions caused by solid food materials. The mucosa is also covered with a layer of mucus secreted by two glands in the lamina propria.
L'endoscopie a longtemps été utilisée pour examiner des parties internes spécifiques du corps qui sont autrement difficiles à visualiser, et encore moins à explorer. L'instrument est composé d'un tube rigide ou flexible avec une lumière à l'extrémité. La lumière sert à fournir un éclairage tandis qu'un système d'objectif ou une caméra transmet des images à un moniteur ou à un spectateur. Dans certains cas, un oculaire est installé à une extrémité de l'endoscope pour permettre au chirurgien de regarder directement dans la partie du corps. Il existe également un canal situé à l'intérieur de l'endoscope qui permet l'insertion d'instruments médicaux fins utilisés pendant la chirurgie.
Qui devrait subir et résultats attendus
Oesophagoscopy is offered to patients suffering from persistent gastroesophageal reflux disease, in which the contents of the stomach and gastric acid go back up the oesophagus. This condition is caused by the weakening or dysfunction of the lower oesophageal sphincter. One of its common symptoms is heartburn, so called because the patient feels a burning sensation starting at the chest and travelling up to the throat. There is also the sensation of food coming back up and leaving an acidic taste in the mouth. Endoscopy can provide information on the extent of damage caused by this disease and helps determine proper treatment management.
Les patients diagnostiqués avec l'œsophage de Barrett peuvent être invités à subir une œsophagoscopie. Cette affection se développe comme une complication du reflux gastro-oesophagien. Le tissu qui tapisse l'œsophage est endommagé en raison de la présence constante d'acide gastrique. Avec le temps, ces tissus ressembleront à ceux qui tapissent l'estomac et pourraient augmenter les risques de développer un adénocarcinome de l'œsophage. L'œsophagoscopie permet de déterminer la progression de la maladie et d'évaluer le protocole de traitement.
L'œsophagoscopie est également utilisée pour diagnostiquer les varices œsophagiennes. Cette condition, qui est souvent causée par cirrhose, se caractérise par la dilatation des veines sous-muqueuses pouvant entraîner des saignements.
Cette procédure convient également aux personnes atteintes de dysphagie, dans lesquelles les patients ont du mal et de la douleur à avaler. Cette condition est plus fréquente chez les personnes âgées qui se plaignent souvent d'avoir l'impression d'avoir de la nourriture coincée dans la gorge. Dans certains cas, les patients ont des nausées lorsqu'ils essaient d'avaler. Si elle n'est pas traitée, elle peut provoquer une malnutrition sévère.
Les patients qui devaient être équipés d'un stent œsophagien doivent également subir une œsophagoscopie. Un stent œsophagien est un tube flexible placé dans l'œsophage pour faciliter le passage des aliments et des liquides de la cavité buccale à l'estomac. En règle générale, les patients chez qui on a diagnostiqué une dysphagie maligne sont équipés de cet appareil, ainsi que ceux souffrant de troubles œsophagiens. fistule, fuites et perforations.
People who have foreign bodies lodged in their throat also need to undergo oesophagoscopy.
Oesophagoscopy is considered a safe procedure for patients who needed to have their oesophagus evaluated and examined. Any foreign body located within the structure can also be pushed to the stomach or completely removed. The tissue collected from the procedure is sent to a pathology lab to determine if further tests or medications are needed.
Le patient peut se voir prescrire un régime mou ou liquide dans les 24 heures suivant la procédure.
Comment se déroule la procédure ?
Le patient est mis sous sédation avant que le médecin insère l'endoscope entre les dents. Le tube est doucement guidé sur la langue et dans l'œsophage. L'épiglotte et les cordes vocales sont correctement visualisées avant d'avancer l'endoscope dans la lumière œsophagienne. Pour gonfler la lumière, du gaz est soufflé doucement dans l'œsophage. Le médecin procède ensuite à un examen attentif de la partie interne de l'œsophage, en notant l'état de la muqueuse. Toute croissance anormale peut également être détectée, ainsi que toute lésion ou partie enflammée de l'œsophage.
L'œsophagoscopie peut également être réalisée en insérant l'endoscope dans les narines. Le patient est appliqué sous anesthésie locale et le tube est inséré doucement. Lorsque le tube atteint le nasopharynx, il est tourné vers le bas pour observer les structures environnantes. L'endoscope est avancé à travers le cou, le patient étant invité à pencher la tête vers la poitrine. Le tube est guidé jusqu'à ce qu'il atteigne la jonction oesophagogastrique. L'endoscope est ensuite tourné et doucement tiré vers l'arrière pendant que le médecin examine la lumière œsophagienne. L'insufflation d'air et l'aspiration facilitent le retrait de l'endoscope.
Risques et complications possibles
La douleur et l'inconfort dans la gorge sont une plainte courante après cette procédure. Le patient fait face au risque de saignement, surtout si la paroi de l'œsophage est blessée. Dans certains cas, des infections peuvent se développer dans la muqueuse. C'est souvent le résultat lorsque la paroi œsophagienne est blessée. Saignement de nez peut survenir chez les personnes subissant une œsophagoscopie nasale. Bien que cela ne se produise que rarement, un patient peut présenter une perforation de la paroi œsophagienne.
En outre, une syncope vasovagale peut survenir dans laquelle le patient s'évanouit en raison du stress et de l'inconfort. Des vomissements et des bâillonnements peuvent également survenir. Le laryngospasme est une autre complication possible. Cette affection se caractérise par de brefs spasmes des cordes vocales pouvant parfois entraîner des difficultés respiratoires. Dans certains cas, le patient est incapable de parler pendant une courte période. Certains patients peuvent se blesser les dents après avoir subi une œsophagoscopie.
Les références:
[Ligne directrice] Comité des normes de pratique de l'ASGE, Evans JA, Early DS, Fukami N, Comité des normes de pratique de l'American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Le rôle de l'endoscopie dans l'œsophage de Barrett et d'autres affections précancéreuses de l'œsophage. Test gastro-intestinal Endosc. 2012 déc. 76 (6):1087-94.
Eliakim R, Sharma VK, Yassin K, et al. Une étude prospective de la précision diagnostique de l'endoscopie par capsule œsophagienne PillCam ESO par rapport à l'endoscopie supérieure conventionnelle chez les patients atteints de reflux gastro-œsophagien chronique. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2005 août 39(7):572-8.
/trp_language]
[wp_show_posts id=””]**Question: What is Oesophagoscopy?**
**Answer:** Oesophagoscopy is a minimally invasive medical procedure used to visualize and examine the lining of the oesophagus, the muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach. It is performed using a thin, flexible tube called an oesophagoscope. The tube is inserted through the mouth, down the oesophagus, and into the stomach. The oesophagoscope is equipped with a camera and a light source, allowing the physician to see the inside of the oesophagus and identify any abnormalities or issues.
**Question: What are the Benefits of Oesophagoscopy?**
**Answer:**
* **Diagnosis:** Oesophagoscopy helps diagnose various conditions affecting the oesophagus, such as ulcers, hiatal hernias, oesophageal varices, and tumours.
* **Identification of Abnormalities:** It allows the physician to detect abnormal growths, inflammation, or narrowing of the oesophagus.
* **Biopsy Collection:** Oesophagoscopy enables the collection of tissue samples (biopsy) from the oesophageal lining for further analysis and diagnosis.
* **Treatment and Intervention:** Oesophagoscopy can be used to perform therapeutic interventions, such as removing foreign objects, widening narrowings (oesophageal dilation), and treating certain types of oesophageal bleeding.
**Question: Who Should Consider an Oesophagoscopy?**
**Answer:**
* Individuals experiencing persistent heartburn, difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), or regurgitation.
* Patients with chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
* Those suspected of having a narrowing of the oesophagus (oesophageal stricture).
* People with suspected tumours or other growths in the oesophagus.
* Individuals with chronic respiratory issues, persistent hoarseness, or an unexplained cough, as it can evaluate potential underlying oesophageal causes.
**Question: What are the Expected Results of Oesophagoscopy?**
**Answer:**
* **Diagnosis**: Oesophagoscopy provides a clear diagnosis for the patient’s oesophageal condition, enabling appropriate and timely treatment.
* **Treatment:** Depending on the findings, therapeutic interventions (e.g., dilation, removal of foreign objects, or treatment of bleeding) can be performed during the procedure.
* **Biopsy Results:** If a biopsy sample was taken during the oesophagoscopy, the results of the analysis will help determine the cause of the issue and guide further treatment decisions.
* **Monitoring:** In cases of ongoing conditions, oesophagoscopy may be repeated to monitor the condition’s progression and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment.







/* Oesophagoscopy: A Comprehensive Guide to Safe and Accurate Upper Gastrointestinal Examination */