What Is a Pediatrician?
Pediatricians are specially trained medical doctors who work with babies, infants, adolescents, and young adults.
Children experience rapid physical, emotional, and behavioral changes as they grow up. Children and teenagers have unique medical needs that might fall outside the expertise of doctors who primarily treat adults.
Continue reading to learn more about pediatricians, including what they do, who they treat, and the qualifications required to become a pediatrician. This article also provides a list of pediatric subspecialties.
What is a pediatrician?
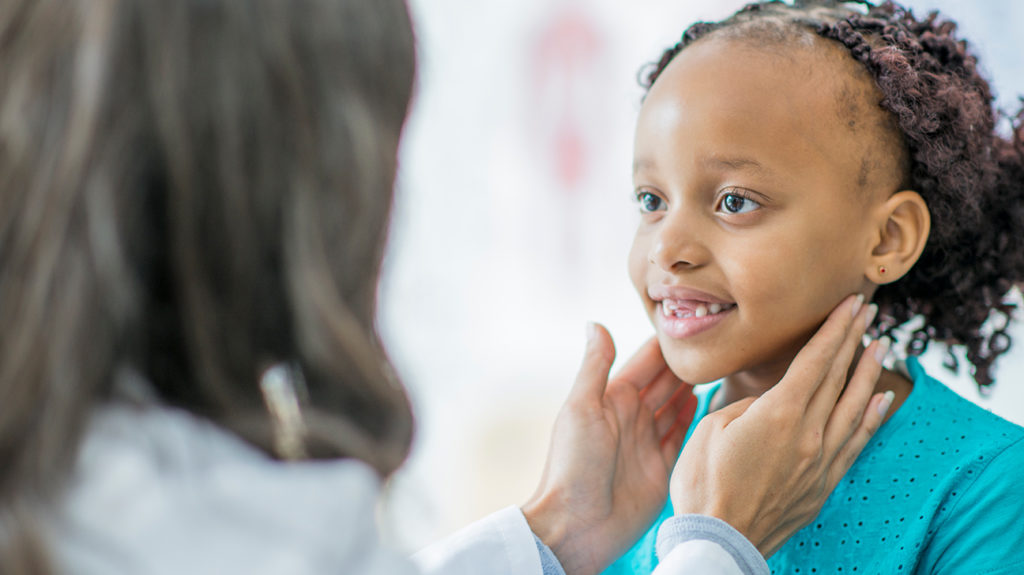
A pediatrician is a medical doctor who specializes in treating infants, children, adolescents, and young adults. Pediatric care can begin before conception and continue through pregnancy.
Children undergo rapid physical and mental changes as they grow. Pediatricians understand this fact and assess a child’s health status based on the normal ranges for their age.
Pediatricians can help diagnose medical conditions in children. Depending on the condition, parents or caregivers may take their children to a primary care pediatrician or a pediatric specialist.
Types
Many pediatricians work as primary care physicians. This type of pediatrician performs regular health and wellness checkups. They also diagnose and treat a wide range of general health conditions, give vaccinations, and offer appropriate health advice to young people and their parents or caregivers.
Other pediatricians specialize in treating specific medical conditions or age ranges. Examples of pediatric subspecialties include the following:
Adolescent medicine specialists
focus on care during adolescence, around 11 to 21 years old.
Critical care pediatricians
facilitate teams of healthcare professionals who treat children in unstable or critical health situations. These pediatricians usually work in hospital-based intensive care units.
Developmental behavioral pediatricians
evaluate the behavioral development of children and teens. Specialists in this field diagnose and treat developmental, learning, and behavioral problems in young people.
Child abuse pediatricians
possess specialized training, experience, and skills necessary for evaluating if a child may have experienced abuse or neglect.
Pediatric oncologists
specialize in diagnosing and treating different types of cancer in children.
Pediatric cardiologists
diagnose and treat various heart conditions in children. Many pediatric cardiologists work closely with pediatric heart surgeons when deciding the best treatment strategies.
Pediatric pulmonologists
diagnose, treat, and manage children who have breathing problems and lung diseases.
Pediatric rheumatologists
treat children and adolescents who have musculoskeletal disorders, such as juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and chronic pain.
Pediatric nephrologists
specialize in treating conditions that affect the urinary system, including urinary tract infections and kidney disease.
Pediatric neurologists
treat and manage neurological disorders in children. Neurological conditions that present during childhood may persist through adulthood. Pediatric neurologists oversee their patients’ care from diagnosis through adolescence.
Neonatal-perinatal pediatricians
provide care to infants before, during, and after birth. They also treat premature and critically ill newborns.
Pediatric gastroenterologists
look after the health of a young person’s digestive system.
Pediatric endocrinologists
specialize in the endocrine system and the hormones it produces. An endocrinologist may treat a variety of conditions in children, including diabetes.
**What Is a Pediatrician?**
**Definition:**
A pediatrician is a medical doctor specializing in the care of infants, children, and adolescents from birth to 21 years of age. They focus on the physical, mental, and behavioral well-being of young patients, providing comprehensive care throughout their developmental stages.
**Scope of Practice:**
Pediatricians are responsible for a wide range of services, including:
* Well-child checkups and immunizations
* Diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic illnesses
* Management of developmental concerns
* Nutrition and feeding guidance
* Injury prevention and treatment
* Behavioral and emotional health support
**Training and Education:**
To become a pediatrician, individuals complete the following steps:
* Obtain a bachelor’s degree in pre-medicine or a related field
* Attend medical school and graduate with a Doctor of Medicine (MD) or Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (DO) degree
* Complete a three-year residency program in pediatrics
* Pass the American Board of Pediatrics certification exam
**Subspecialties:**
Within the field of pediatrics, numerous subspecialties exist, including:
* Neonatology (care of newborns)
* Pediatric cardiology (heart conditions)
* Pediatric oncology (cancer treatment)
* Pediatric nephrology (kidney disease)
* Pediatric gastroenterology (digestive system disorders)
**Role in Patient Care:**
Pediatricians play a vital role in ensuring the optimal health and well-being of young patients. They provide comprehensive and age-appropriate care, promoting healthy development and preventing or treating various medical conditions.
**Importance:**
Pediatricians are essential healthcare providers for children and adolescents, as they possess specialized knowledge and expertise in dealing with the unique health challenges and developmental needs of this population.





A pediatrician is a medical doctor who specializes in the care of children and adolescents.